中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (20): 3770-3776.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.20.022
• 组织构建临床实践 clinical practice in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
杜氏进行性肌营养不良患儿常速行走的步态特征
陈 楠1,杜 青1,刘晓青1,李西华2,伍 勰3,周 璇1,张树新1
- 1上海交通大学附属新华医院,上海市 200092
2复旦大学附属儿科医院,上海市 201100
3上海体育学院,上海市 200438
Gait characteristics of Duchenne muscular dystrophy children at normal speeds
Chen Nan1, Du Qing1, Liu Xiao-qing1, Li Xi-hua2, Wu Xie3, Zhou Xuan1, Zhang Shu-xin1
- 1 Xinhua Hospital of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200092, China
2 Pediatric Hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai 201100, China
3 Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai 200438, China
摘要:
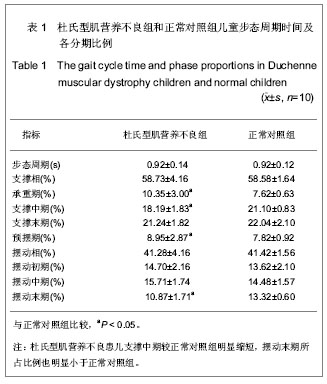
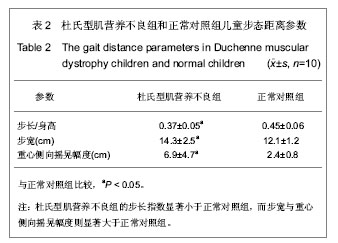
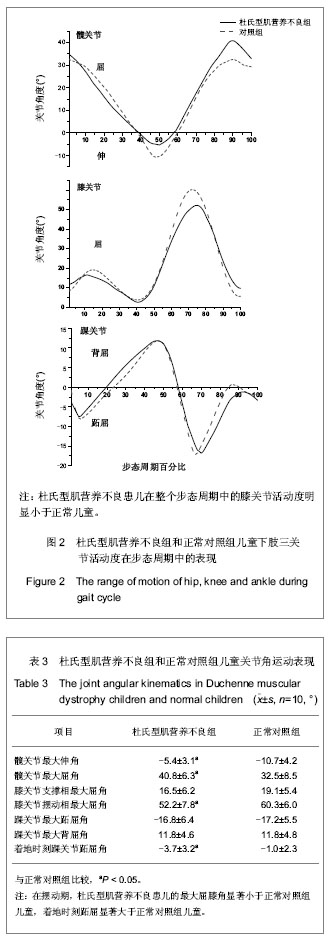
背景:对杜氏进行性肌营养不良患儿异常步态的生物力学研究目前尚不多见,且缺乏步态的足底压力特征结果报道。 目的:分析杜氏进行性肌营养不良患儿常速行走的步态运动学及足底压力分布特征。 方法:利用VICON红外光点捕获系统,采集10名杜氏进行性肌营养不良患儿及10名正常儿童裸足常速行走的三维运动学数据,并利用Medilogic足底压力测试系统记录支撑足的足底压力分布数据。 结果与结论:杜氏型肌营养不良组行走时的步长明显小于正常对照组,而步宽和重心摇晃幅度则大于正常对照组;杜氏型肌营养不良组步态的双支撑期所占的周期比例大于正常对照组,摆动末期所占的周期比例则小于正常对照组;杜氏型肌营养不良组髋关节最大伸角小于正常对照组,髋关节最大屈角大于正常对照组,摆动相最大膝屈角小于正常对照组,着地时踝关节跖屈角大于正常对照组;杜氏型肌营养不良组在行走过程中最大足底压力小于正常对照组,最大压力的分布向足前区外侧偏移。结果表明,步态周期时间百分比可作为杜氏型肌营养不良患儿行走能力的评价指标,杜氏型肌营养不良患儿在常速行走过程中所表现出的各种非正常的步态特征可能归因于下肢各关节伸肌群力量不足,部分患儿踝关节呈明显的马蹄足内翻也是造成步态异常的重要原因之一。
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)